Regression: Torch as a Tensor library¶
回归问题是一种寻找自变量与因变量之间的关系的统计建模方法。
设有自变量 \(\boldsymbol{x}\) 和因变量 \(y\) 符合 \(y = g(\boldsymbol{x})\),则回归的任务是找到一个 \(f(\cdot)\),\(\mathrm{s.t.} \min{\mathrm{dist}(f(\boldsymbol x), g(\boldsymbol x))}\)。
较为常用的,也是最简单的,是线性回归模型。虽然单变量线性回归在中学已经学过解析解了
线性回归假设自变量与因变量成线性关系,也就是
\[
H(x) = Wx+b
\]
由此关系我们构造 cost function:
\[
\begin{gathered}
cost=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(H\left(x^{(i)}\right)-y^{(i)}\right)^{2} \\
H(x)=W x+b
\end{gathered}
\]
其中 \(W\) 和 \(b\) 被称为参数,故也可以写作
\[
\operatorname{cost}(W, b)=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(H\left(x^{(i)}\right)-y^{(i)}\right)^{2}
\]
目标函数就是:
\[
\min_{W, b} \operatorname{cost}(W, b)
\]
读作 Minimize \(\operatorname{cost}(W, b)\) with regard to \(W\) and \(b\).
那么比如我们拿到了~西瓜~数据
| x | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
对于每对 \((x, Y)\) 我们都可以计算 \(\mathrm{cost}\)。
这里利用 PyTorch 进行计算。
import torch
import numpy as np
def cost(W: torch.Tensor, x: torch.Tensor, y: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = x.unsqueeze(-1)
y = y.unsqueeze(-1)
return torch.mean(torch.square(W * x - y), (0,))
x = torch.tensor([1., 2., 3.])
y = torch.tensor([1., 2., 3.])
print(cost(W, x, y)) # tensor(4.6667)
W = torch.ones(3)
print(cost(W, x, y)) # tensor(0.)
W = torch.full((3,), 2)
print(cost(W, x, y)) # tensor(4.6667)# What does cost(W) look like?
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = torch.arange(-3., 5., 0.01)
inp = torch.stack([rng]*3)
output = cost(inp, x, y)
plt.plot(rng.numpy(), output.numpy())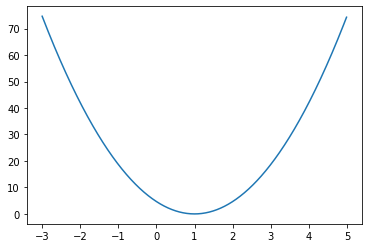
问题是:如何最小化这个损失函数?
解析解是这样的:
\[
\operatorname{cost}(W)=\frac{1}{2 m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(W x^{(i)}-y^{(i)}\right)^{2}
\]
则求偏导
\[
\frac{\partial }{\partial W}\mathrm{cost}(W) = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} x^{(i)} \left(W x^{(i)}-y^{(i)}\right)
\]
虽然这个简单的方程有解析解,但对于大多数优化问题来说是没有解析解的。在此节中我们将学习如何利用梯度下降法求解回归问题。
\[
\begin{gathered}
W:=W-\alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial W} \operatorname{cost}(W) \\
W:=W-\alpha \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(W x^{(i)}-y^{(i)}\right) x^{(i)}
\end{gathered}
\]
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(42)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class FakeDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self):
super(FakeDataset, self).__init__()
k = np.random.random()
self.x = x = np.arange(1, 4)
b = np.arange(1, 4)
self.val = k * x + b
# print("Guess: ", k, b)
self.data = list(zip(x, k*x+b))
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.data[index]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data);
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.k = torch.tensor(10000., requires_grad=True)
self.b = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
def forward(self, input):
return input * self.k + self.b
def loss_fn(out, target):
return (out-target)**2
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset = FakeDataset()
model = Net()
tb = SummaryWriter(log_dir="runs")
step = 1
lr = 0.01
EPOCHS = 1000
for epoch in range(1, EPOCHS):
for x, val in dataset:
out = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(out, val)
model.k.grad = None
model.b.grad = None
loss.backward()
with torch.no_grad():
tb.add_scalar("Loss", float(loss), step)
step+=1
model.k -= lr*model.k.grad
model.b -= lr*model.b.grad
plt.scatter(dataset.x, dataset.val)
eval_out = model(torch.tensor(np.arange(1, 11)))
plt.plot(np.arange(1, 11), eval_out.detach().numpy())
plt.show()
最后更新:
2023-01-31